Mini gyro will explore Phobos moon
Silicon Sensing Systems is to supply a miniature gyro for a mission to Mars, writes Nick Flaherty.
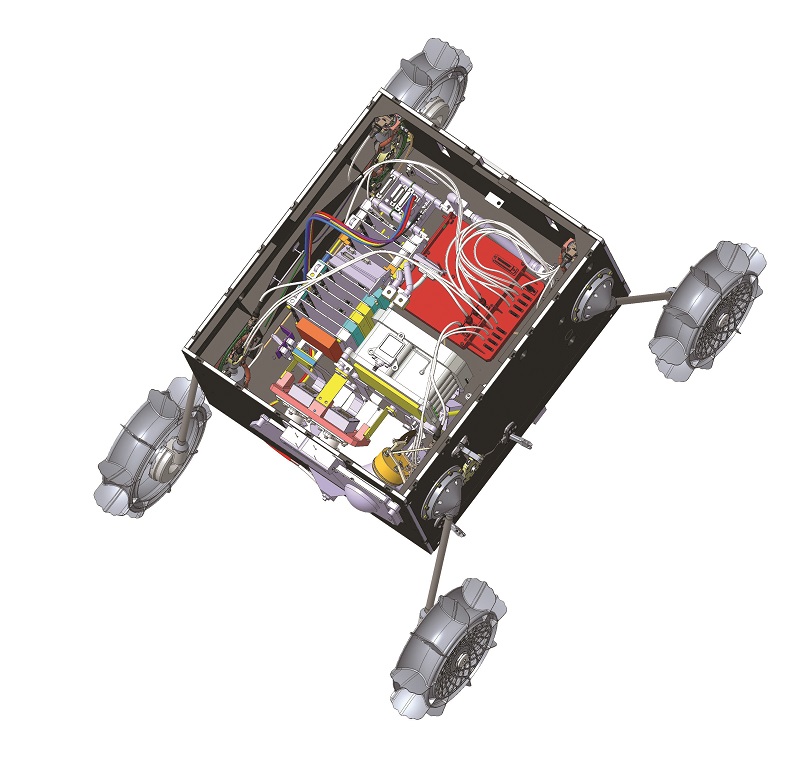
Two of the CRM200 gyros will be used by the German Aerospace Center (DLR) for use in the Martian Moons eXploration (MMX) mission being run by the Japanese space agency, JAXA. This mission will travel to Mars and the two gyros will be used in a 25 kg rover vehicle that will explore the larger of its moons, Phobos.
The rover is being developed by DLR and the French CNES research agency to collect samples ready for the return to Earth.
The Pinpoint gyros will be used to detect any unintended movements of the rover on the unknown surface. Depending on the initial checkout of the drivetrain, which includes the gyros, an optional safety module will be activated in the software to automatically prevent instability during the rover’s drive sessions.

The 5 mm x 6 mm Pinpoint single-axis gyros are hermetically sealed in a ceramic LCC surface-mount package for temperature and humidity resistance with integrated temperature sensor.
The gyros have successfully completed total iodising dose (TID) testing at 17kRad Radiation and Proton tests (up to 68 MeV proton) for use in space.
The gyro uses a micromachined sensor to precisely measure angular rate with a low bias instability (12º/hr) over a short integration period of under 1 s. The dynamic range is selectable at 75º/s, 150º/s, 300º/s and 900º/s.
After observation and sample collection, the spacecraft will return to Earth carrying the material from Phobos. The current schedule has a launch date in 2026, followed by a Martian orbit insertion in 2027, returning to Earth in 2031.
UPCOMING EVENTS
























