AI control for ballbots
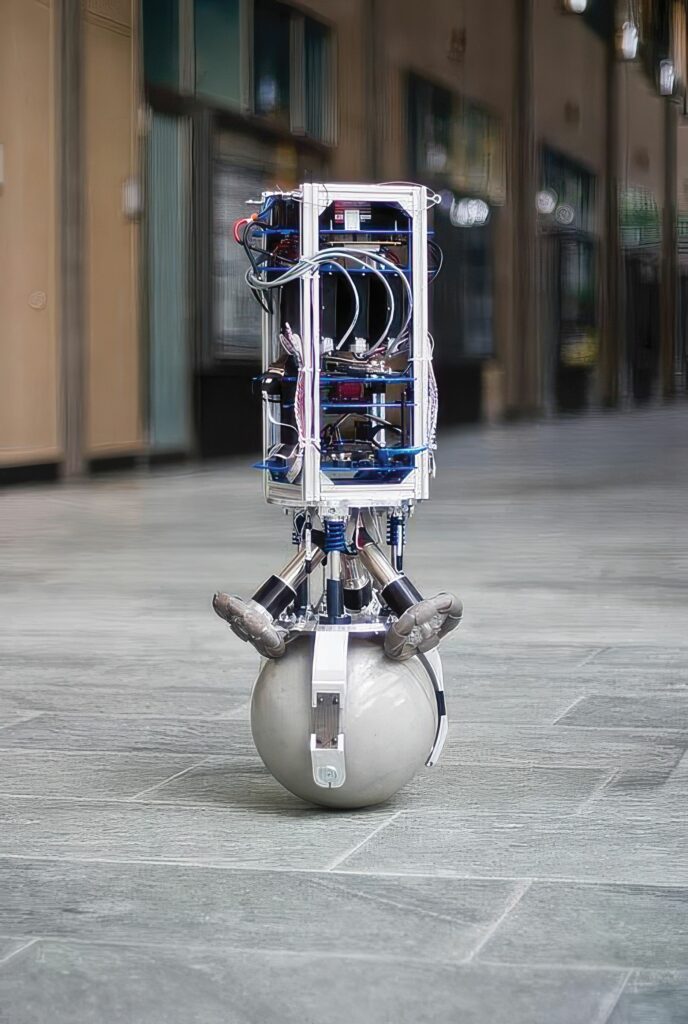
(Image courtesy of Hanoi University of Industry)
Researchers in Asia have developed a new technique with machine learning for controlling ballbots, writes Nick Flaherty.
Ballbots are versatile robotic systems with the ability to move around in all directions. This makes it tricky to control their movement.
The team in Vietnam and Japan developed the technique that can be combined with machine learning to provide balance and stability.
This uses a proportional integral derivative (PID) controller with a non-linear response that, combined with a neural network, can robustly control the ballbot motion.
PID controllers are widely used as a feedback-based control loop mechanism to manage machines and processes that require continuous control and automatic adjustment. It is typically used in industrial control systems where constant control through modulation is necessary.
The non-linear PID (NPID) is combined with a radial basis function neural network (RBFNN) that requires only lightweight computation to provide stability and reduce chattering from the feedback loop, a common problem with ballbots.
An adaptive control law is improved continuously using the neural network to handle the real-time estimation of the external force on the ballbot.
Through both simulations and real-world experiments, the team showed that the NPID-RBFNN controller outperforms traditional PID and NPID controllers. By minimizing unnecessary movements and chattering, the proposed controller can also reduce energy consumption.
“Ballbots with this advanced controller can be used as assistive robots for tasks requiring high mobility and precision. They can also be used as service robots in dynamic settings such as restaurants, hospitals, or airports, offering smooth navigation,” said Dr. Van-Truong Nguyen of Hanoi University of Industry, Vietnam, who led the project.
UPCOMING EVENTS
























